CELL
- all living organisms are made of cells as the smallest functional unit.
CELL THEORY
- The cell is the fundamental unit of structure and function in living things.
- All organisms are made up of one or more cells.
- Cells arise from other cells through cellular division.
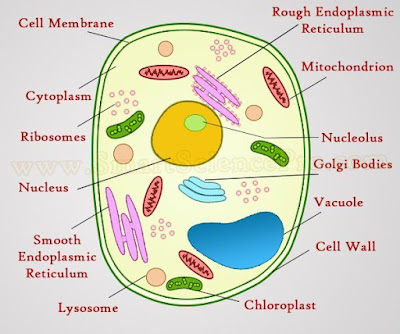
Figure: 1.1 structure of a cell
Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is a thin outer membrane, which maintains
the integrity of the cell. It keeps the cell and its contents
separate and distinct from the surrounding. It is a double-layered measuring about 4.5 nm and made of phospholipids,
cholesterol, glycolipids, & carbohydrate (oligosaccharides).
The bi-layer is self-sealing. If a needle is injected and pulled
out, it automatically seals.
Functions: -
1. Separate the cytoplasm inside a cell from the extracellular
fluid.
2. Separate cell from one another
3. Provide an abundant surface on which chemical reaction
can occur.
4. Regulate the passage of materials in to and out of cells. It
also let some things in and keeps others out. The quality
selective permeability

Cytoplasm is a thick solution that fills each cell and is enclosed by the cell membrane. It is mainly composed of water, salts, and proteins. In eukaryotic cells, the cytoplasm includes all of the material inside the cell and outside of the nucleus. All of the organelles in eukaryotic cells, such as the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria, are located in the cytoplasm. The portion of the cytoplasm that is not contained in the organelles is called the cytosol. Although cytoplasm may appear to have no form or structure, it is actually highly organized. A framework of protein scaffolds called the cytoskeleton provides the cytoplasm and the cell with their structure
Ribosome
A ribosome is a complex cellular mechanism used to translate
genetic code into chains of amino acids. Long chains of amino acids fold and function as proteins in cells.
Nucleus
The nucleus is where the DNA is kept and RNA is transcribed. RNA is moved out of the nucleus through the nuclear pores. Proteins needed inside the nucleus are transported in through the nuclear pores. The nucleolus is usually visible as a dark spot in the nucleus, and is the location of ribosome formation.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are where RNA is translated into protein. This process is called protein synthesis. Protein synthesis is very important to cells, therefore large numbers of ribosomes are found in cells. Ribosomes float freely in the cytoplasm, and are also bound to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). ER bound to ribosomes is called rough ER because the ribosomes on the ER give it a rough sandpaper like look.. These organelles are very small, made up of 50 proteins and several long RNAs bound together. Ribosomes do not have a membrane. Ribosomes fall into two seperate units while not synthesizing protein.
Endowplasmic reticulum
endoplasmic reticulum is the transport system for molecules needed for certain changes and specific destinations, instead of molecules that float freely in the cytoplasm. There are two types of ER, rough and smooth. Rough ER has ribosomes attached to it, as mentioned before, and smooth ER does not.
Lysosome
The
lysosome is the digestive system in the cell. It breaks down molecules into their base components digestive enzymes. This demonstrates one of the reasons for having all parts of a cell compartmentalized, the cell couldnt use the destructive enzymes if they werent sealed off from the rest of the
The
cytoplasm was defined earlier as the material between the plasma membrane (cell membrane) and the nuclear envelope. Fibrous proteins that occur in the cytoplasm, referred to as the cytoskeleton maintain the shape of the cell as well as anchoring organelles, moving the cell and controlling internal movement of structures.
Microtubules function in cell division and serve as a "temporary scaffolding" for other organelles. Actin filaments are thin threads that function in cell division and cell motility. Intermediate filaments are between the size of the microtubules and the actin filaments.eeze-fracturing is able to split the bilayer.
Vacuoles are single-membrane organelles that are essentially part of the outside that is located within the cell. The single membrane is known in plant cells as a tonoplast. Many organisms will use vacuoles as storage areas. Vesicles; are much smaller than vacuoles and function in transport within and to the outside of the cell.
The
golgi bodies changes molecules and divides them into small membrane contained sacs called vesicles. These sacs can be sent to various locations in the cell.Golgi Complexes (follow the link to the MIT Hypertextbook page on Golgi) are flattened stacks of membrane-bound sacs. They function as a packaging plant, modifying vesicles from the Rough ER. New membrane material is assembled in various cisternae of the golgi.
Like mitochondria,
chloroplasts have their own DNA, termed cpDNA. Chloroplasts of Green Algae (Protista) and Plants (descendants of some Green Algae) are thought to have originated by endosymbiosis of a prokaryotic alga similar to living
Prochloron(Prochlorobacteria). Chloroplasts of Red Algae (Protista) are very similar biochemically to cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green bacteria [algae to chronologically enhanced folks like myself :)]). Endosymbiosis is also invoked for this similarity, perhaps indicating more than one endosymbiotic event occurred.
Mitochondria are a part of tissue cells that consists of an outer and an inner membrane. The mitochondria are the main energy source of the cell, in fact, they are often called the "power plants" of the body because this is where energy (ATP) is created. Uncoupled thermogenesis also occurs in the mitochondria; any of the very tiny rodlike or stringlike structures that occur in nearly all cells of plants and animals, and that process food for energy



👍👍
ReplyDelete